Ports List | Back | Foward
Edge MSE
45 R-0
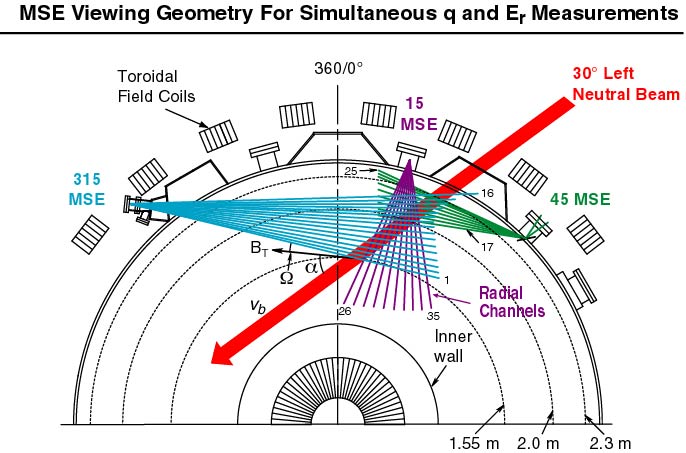
Motional Stark Effect (MSE) Diagnostic
The main purpose of MSE is to measure the profile of the magnetic field pitch angle (or equivalently the current density profile) in tokamak plasmas. In conjunction with the equilibrium code EFIT, this information allows the safety factor, q,to be determined which is important for the understanding of both stability and confinement in tokamaks. The MSE system can also provide information on the profile of the radial electric field, Er.
The MSE technique relies upon the Stark splitting of the Balmer alpha line emitted from high-energy neutral hydrogen (or deuterium) atoms injected into the plasma. The neutral atoms experience a large Lorentz electric field E=v x B due to their motion across the plasma magnetic field. The strong electric field causes a splitting of the alpha emission into 9 distinct lines with two polarization states, π and σ. The π and σ states are polarized parallel and perpendicular to the electric field respectively. By measuring the polarization angle of the light emission, and knowing the beam injection velocity vector, v, one can then deduce the pitch angle of the magnetic field.
The MSE diagnostic is sensitive to the background electric field in the plasma as well as the motional v x B field of the high-energy beam atoms. In most plasmas with lower pressure gradients and rotation velocities, the v x B field is much larger than the plasma Er, so Er can be neglected.
